Module 59 - A322a
A322a: Understanding User Needs for Transportation Field Cabinet Systems Using ATC 5301 v02
HTML of the Student Supplement
(Note: This document has been converted from the Student Supplement to 508-compliant HTML. The formatting has been adjusted for 508 compliance, but all the original text content is included, plus additional text descriptions for the images, photos and/or diagrams have been provided below.)
A322a: Understanding User Needs for Transportation Field Cabinet Systems Using ATC 5301 v02
Table of Contents
Module Description - 2
Introduction/Purpose - 2
Samples/Examples - 3
Reference to Other Standards - 9
Glossary - 9
References - 10
Study Questions - 11
1. Module Description
This module is the first in a set of modules on the ATC 5301 ATC Cabinet Standard v02. It has the following recommended prerequisites in the ATC curriculum for students taking this course.
- A207a: Building an ITS Infrastructure Based on the ATC 5201 Standard Part 1 of 2
- A207b: Building an ITS Infrastructure Based on the ATC 5201 Standard Part 2 of 2
- A208: Using the ATC 5401 Application Programming Interface Standard to Leverage ITS Infrastructures
- A307a: Understanding User Needs for Advanced Transportation Controllers Based on ATC 5201 Standard v06
- A307b: Understanding Requirements for Advanced Transportation Controllers Based on ATC 5201 Standard v06
2. Introduction/Purpose
The Advanced Transportation Controller (ATC) family of standards provides an open architecture hardware and software platform that can support a wide variety of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) field applications including traffic management, safety, security, and other applications. These standards are characterized by their modularity, support of multiple and current application programs, and designed to facilitate the adoption of new technologies. There are three standards within the ATC program: the ATC 5201 ATC Standard, the ATC 5401 Application Programming Interface (API) Standard, and the ATC 5301 ATC Cabinet Standard.
The focus of this module is on the recently approved ATC 5301 ATC Cabinet Standard v02. This module discusses the advantages of transportation field cabinet systems that conform to the standard. It presents the structure and key elements of the standard. It helps users identify and write user needs for ATC Cabinets which helps to justify and support an ATC Cabinet specification.
At the conclusion of this module, students will be able to:
- Explain the advantages of transportation field cabinet systems based on the ATC 5301 Standard v02;
- Describe the structure of the ATC 5301 Standard v02;
- Identify and write user needs for ATC Cabinet systems; and
- Create a concept of operations that includes ATC Cabinets.
3. Samples/Examples
Table 1. Input/Output Channels for Transportation Field Cabinet Systems.
| TFCS | Physical Mounting | Internal Bus | Signal Monitor | Input Channels | Monitored Output Channels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC Cabinet v02 | Rack and Shelf | Serial 614.4 kbps | Cabinet Monitor Unit | 120 | 32 |
| ITS Cabinet v01 | Rack | Serial 614.4 kbps | Cabinet Monitor Unit | 120 | 28 |
| NEMA TS-2 | Shelf | Serial 153.6 kbps | Malfunction Management Unit | 64 | 16 |
| Caltrans Model 33X | Rack | Parallel/Discrete Wiring | Conflict Monitor | 44 | 16/18 |
| NEMATS-1 | Shelf | Parallel/Discrete Wiring | Conflict Monitor | 8 | 3/6/12/18 |
Table 2. Requirement traceability example from ATC 5201 Standard v02.
| Verify the Requirement | |||||||
| Requirement ID | Requirement Title | ||||||
| 5.4.3.1 | Two Output Channels per HDSP120 | ||||||
|
Requirement Text The HDSP120 shall have two output channels. |
|||||||
|
Justification for the Requirement: 1. The user needs the TFCS to support the use of output device? that have higher channel density than the commonly deployed field output devices. |
|||||||
|
Source for Justification: 1. UN ID 4.3.4.1 |
|||||||
|
Requirement Text (Comments/Changes) Guidance: |
|||||||
|
Related Design Elements 1. 6.2 Model 2202 High Density Switch Pack / Flasher Unit (HDSP/FU) |
|||||||
| Requirement Criteria | Yes | No | |||||
| 1 | Is the justification/basis for the requirement clear and valid? | X | |||||
| 2 | Is the requirement well-formed? | X | |||||
| 3 | Is the requirement unambiguous? | X | |||||
| 4 | Is the requirement feasible? | X | |||||
| 5 | Is the requirement verifiable? | X | |||||
| Insp. | Anal. | Test | Demo. | ||||
| 6 | If verifiable, by which method? | X | |||||
| Note: An answer of no requires a comment or change in the Comments/Change field of the 'Requirement Text' section above. | |||||||
Table 3. Requirement traceability example from ATC 5201 Standard v02.
| Verify the Requirement | |||||||
| Requirement ID | Requirement Title | ||||||
| 5.4.4 | Low Voltage Switch Pack Modules | ||||||
|
Requirement Text The following power limitations shall apply to the Low Power / Low Voltage cabinet option
|
|||||||
|
Justification for the Requirement: 1. The user needs the TFCS to provide for field wiring that is at voltage and current levels below those dangerous to humans. |
|||||||
|
Source for Justification: 1. UN ID 4.3.4.2 |
|||||||
|
Requirement Text (Comments/Changes) Guidance: |
|||||||
Related Design Elements
|
|||||||
| Requirement Criteria | Yes | No | |||||
| 1 | Is the justification/basis for the requirement clear and valid? | X | |||||
| 2 | Is the requirement well-formed? | X | |||||
| 3 | Is the requirement unambiguous? | X | |||||
| 4 | Is the requirement feasible? | X | |||||
| 5 | Is the requirement verifiable? | X | |||||
| Insp. | Anal. | Test | Demo. | ||||
| 6 | If verifiable, by which method? | X | |||||
| Note: An answer of no requires a comment or change in the Comments/Change field of the “Requirement Text” section above. | |||||||
Table 4. Requirement traceability example from ATC 5201 Standard v02.
| Verify the Requirement | |||||||
| Requirement ID | Requirement Title | ||||||
| 5.13.1 | Diagnostic Display Local Display | ||||||
|
Requirement Text The TFCS shall contain a Diagnostic Display Unit (DDU) which supports local display of both historical and current cabinet status and log data collected by the monitoring subsystem. |
|||||||
|
Justification for the Requirement: 1. The user needs the TFCS to be of a design that reduces the time required for maintenance personnel to perform maintenance actions in the field. |
|||||||
|
Source for Justification: 1. UN ID 4.3.1.20 |
|||||||
|
Requirement Text (Comments/Changes) Guidance: |
|||||||
|
Related Design Elements 1. 6.5 Model 2220 Auxiliary Display Unit |
|||||||
| Requirement Criteria | Yes | No | |||||
| 1 | Is the justification/basis for the requirement clear and valid? | X | |||||
| 2 | Is the requirement well-formed? | X | |||||
| 3 | Is the requirement unambiguous? | X | |||||
| 4 | Is the requirement feasible? | X | |||||
| 5 | Is the requirement verifiable? | X | |||||
| Insp. | Anal. | Test | Demo. | ||||
| 6 | If verifiable, by which method? | X | |||||
| Note: An answer of no requires a comment or change in the Comments/Change field of the 'Requirement Text' section above. | |||||||

Figure 1: High Level Functional Block Diagram, High Voltage Version
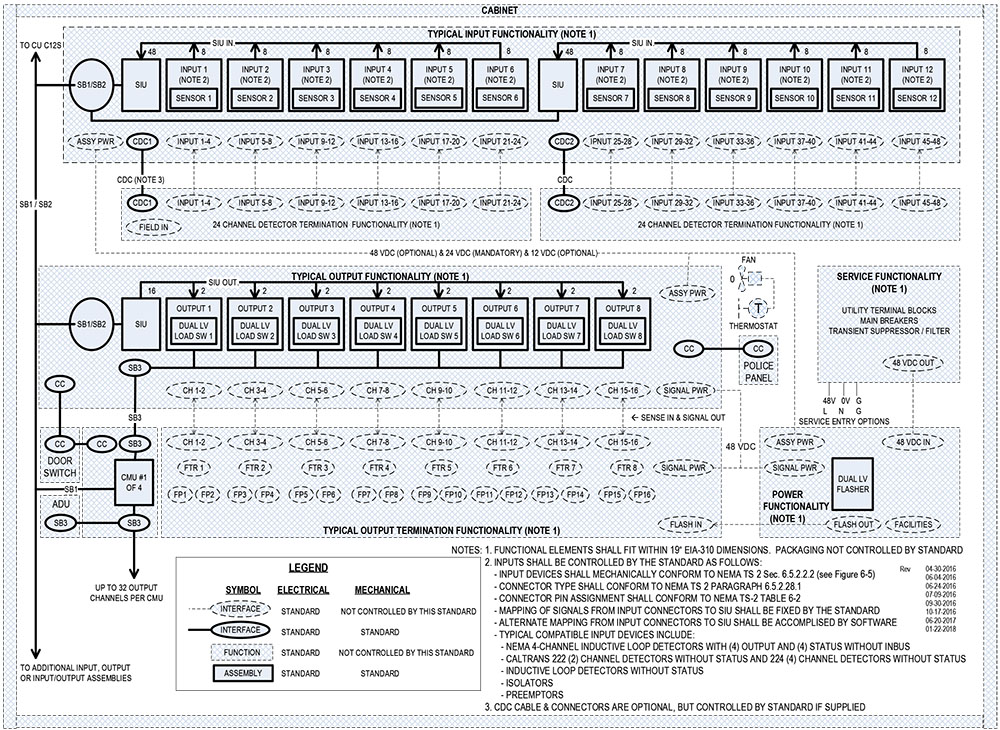
Figure 2: High Level Functional Block Diagram, Low Voltage Version
4. Reference to Other Standards
-
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, IEEE 29148-2018 - ISO/IEC/IEEE International Standard - Systems and software engineering -- Life cycle processes --Requirements engineering. IEEE, 2018.
https://standards.ieee.org/standard/29148-2018.html -
Institute of Transportation Engineers, ATC5201 Advanced Transportation Controller (ATC) Standard Version 06.25. ATC Joint Committee, Recommended Standard, January 12, 2018.
https://www.ite.org/technical-resources/standards/ -
Institute of Transportation Engineers, Recommended Standard ATC 5201 Advanced Transportation Controller (ATC) Standard Version 06A. ATC Joint Committee, Recommended Standard, January 2020.
https://www.ite.org/technical-resources/standards/atc-controller/version-6/ -
Institute of Transportation Engineers, ATC5301 Advanced Transportation Controller (ATC) Cabinet Standard Version 02. ATC Joint Committee, March 18, 2019.
https://www.ite.org/technical-resources/standards/its-cabinet/version-2/ -
Institute of Transportation Engineers, ATC5401 Application Programming Interface (API) Standard for the Advanced Transportation Controller (ATC) v02.17. ATC Joint Committee, September 15, 2013. (Note same as September 1, 2011.)
https://www.ite.org/technical-resources/standards/atc-api/ - Institute of Transportation Engineers, Recommended Standard ATC 5401 Application Programming Interface (API) Standard for the Advanced Transportation Controller (ATC) v02A. ATC Joint Committee, January 2020.
-
Institute of Transportation Engineers, Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) Standard Specification for Roadside Cabinets v01.02.17b. ATC Joint Committee, 16 November 2006
https://www.ite.org/technical-resources/standards/its-cabinet/version-1-02-17b/ - National Electrical Manufacturers Association, NEMA Standards Publication TS-1-1989 Traffic Control Systems. NEMA, 1989.
- National Electrical Manufacturers Association, NEMA TS-2-2016 Traffic Controller Assemblies with NTCIP Requirements Version 03.07. NEMA, 2016
5. Glossary
To include additional descriptions/acronyms used primarily in the module. List out in alphabetical order.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| AASHTO | American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials |
| AC | alternating current |
| ATC | Advanced Transportation Controller |
| ATCC | ATC Cabinet |
| CB | Circuit Breaker |
| CBD | Central Business District |
| ConOps | Concept of Operations |
| DC | direct current |
| EMI | electromagnetic interference |
| ESD | Electrostatic Discharge |
| FHWA | Federal Highway Administration |
| GFI | Ground Fault Interrupt |
| I/F | interface |
| I/O | input/output |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| IMSA | International Municipal Signal Association |
| IPC | Formerly, the Institute for Printed Circuits. This same institution was later called the Institute Interconnecting and Packaging Electronic Circuits. It is now referred to as IPC-Association Connecting Electronics Industries. |
| ITE | Institute of Transportation Engineers |
| ITS | Intelligent Transportation System |
| JPO | Joint Program Office |
| LED | light emitting diode |
| MTBF | mean time between failures |
| NEC | National Electrical Code |
| NEMA | National Electrical Manufacturers Association |
| NFPA | National Fire Protection Association |
| NRTL | Nationally Recognized Testing Lab |
| NTCIP | National Transportation Communications for ITS Protocol |
| PF | power factor |
| RFI | radio frequency interference |
| SDO | Standard Development Organization |
| SEMP | System Engineering Management Plan |
| SEP | Systems Engineering Process |
| SSC | Small-Sized Cabinet |
| StdHLD | Standards High Level Design |
| StdRS | Standards Requirements Specification |
| TFCS | transportation field cabinet system |
| UPS | Uninterruptible Power Source |
| USA | United States of America |
| USDOT | United States Department of Transportation |
| VAC | voltage alternating current |
| VDC | voltage direct current |
| WG | Working Group |
6. References
-
California Department of Transportation, Caltrans Transportation Electrical Equipment Specifications (TEES). California Department of Transportation, 12 March 2009
http://www.dot.ca.gov/trafficops/tech/docs/TEES2009.pdf -
Institute of Transportation Engineers,
ITS Cabinet V2 Standards Requirements Specification (StdRS) v01.04. ATC Joint Committee, 31 January 2019.
https://www.ite.org/technical-resources/standards/its-cabinet/version-2/
7. Study Questions
The quiz/poll questions and answer choices as presented in the PowerPoint slide to allow students to either follow along with the recording or refer to the quiz at a later date in the supplement.
1. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of using the ATC Cabinet Standard?
- Low voltage option for 48 VDC on field wires
- Touch Safe Design
- Functional standard except where interchangeability desired
- Same number of channels per switch pack as ITS Cabinet v01
2. True or False? The High Level Functional Block Diagram identifies how the ATC Cabinet functions perform actuated signal control.
- True
- False
3. Which of the following is a correct statement?
- Rationale of user needs have proposed solutions
- User needs must testable
- A user need is a major desired capability
- Only needs in ATC 5301 v02 are valid for a spec
4. Which of the following is a benefit of building a ConOps for an ATC Cabinet?
- Provides justification for investment in ATC Cabinets
- Only technical stakeholders are necessary to produce it
- Strategic or regional plans are unnecessary
- Organization of user needs is the same for all agencies