Goals
- Establish a reasonable root certificate expiration period by shortening the EE Enrollment certificate expiration period from previous 30 years as mentioned in the Vehicle Safety Communications Security Studies Project (VSCS)
- Allow EE to use their existing enrollment certificate for authentication when requesting a rollover enrollment (Re-enrollment) certificate
- Minimize the number of root certificates that are valid at any time
Assumptions
-
Vehicles have an estimated life of up to 30 years
-
EEs may only have connectivity once every three years
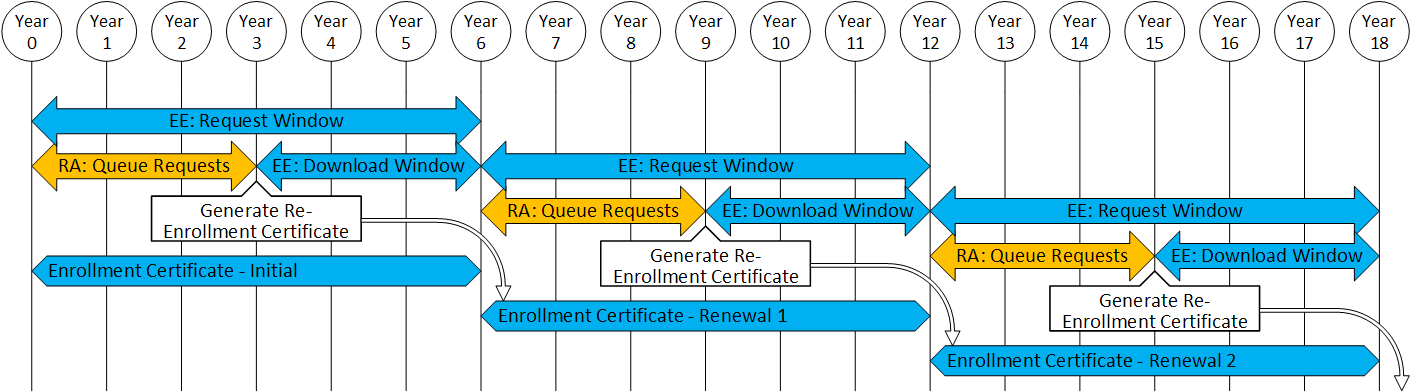
- Initial EE enrollment certificates and rollover certificates are issued by the ECA
- Only one enrollment certificate for an EE shall be valid at a time
- EE must request and download the rollover certificate before the current certificate expires
- Re-enrollment certificates will not be generated or available for download until three years before the expiration of the current enrollment certificate
Factors Influencing Certificate Lifetimes
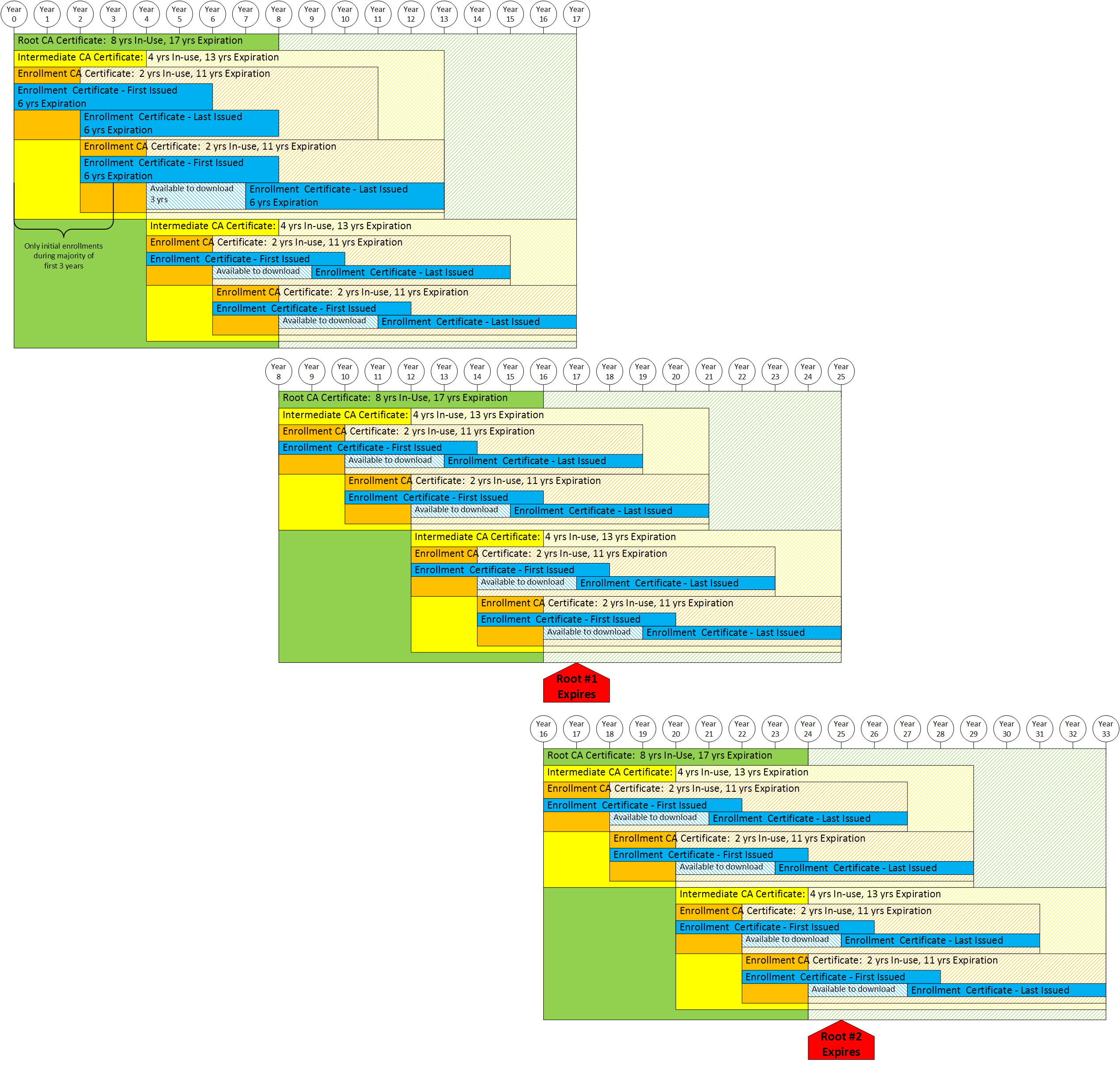
Certificate lifetimes affect the security of PKI infrastructures. The longer a public/private key pair is in use, the greater the chances are that the keys can be compromised. As computing power increases and technologies improve over time, cryptanalysis becomes a risk. For these reasons, excessively long-lived CA certificate lifetimes are undesirable.
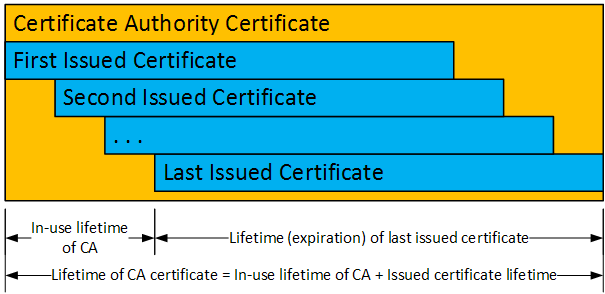
The below diagram illustrates the calculation of the minimum lifetime of a typical CA certificate.
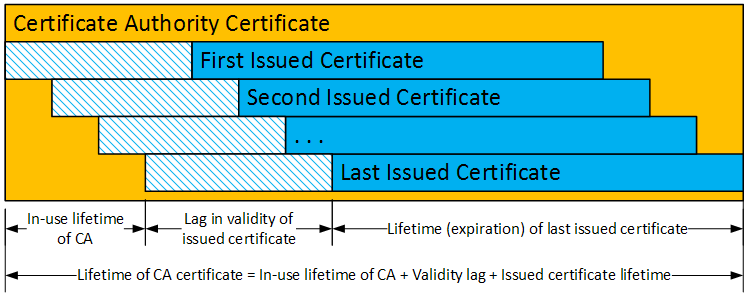
Some certificate authorities may issue certificates that are not valid until a significant time in the future. Examples of this within the SCMS are pseudonym certificates and rollover enrollment certificates. As a recommendation, the validity lag for these certificates can be up to 3 years. For example, a pseudonym certificate generated (issued) today may have a "Valid from" date that is up to 3 years from now. The below diagram illustrates the impact of the validity lag on the lifetime of the issuing CA certificate.
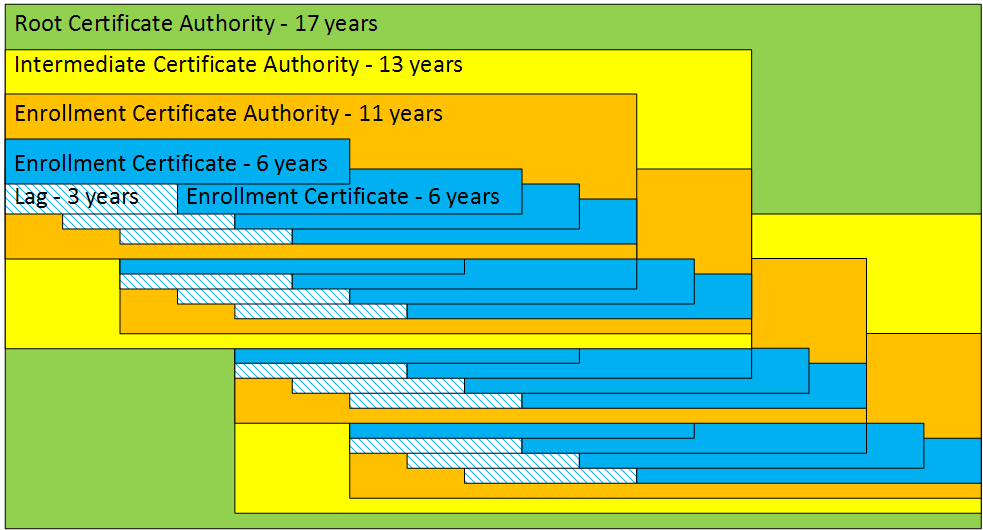
As additional layers are added to the certificate hierarchy, this process is repeated up to the root CA. When operational factors and the requirement to have the ability to issue new certificates at any time are considered, the required lifetime of each CA certificate in the trust chain is further increased.
It will be necessary to renew the enrollment certificate multiple times for an estimated vehicle lifetime of 30 years. An enrollment certificate lifetime of 6 years greatly reduces security concerns due to certificate longevity, but it requires an automatic renewal mechanism that can accommodate the EEs with infrequent network connectivity. As better and more frequent network connectivity becomes available to the EEs, it may be possible to further reduce these lifetimes.
The below diagram illustrates the impact of issued certificate lifetime, certificate validity lag and operational factors on the PKI hierarchy.
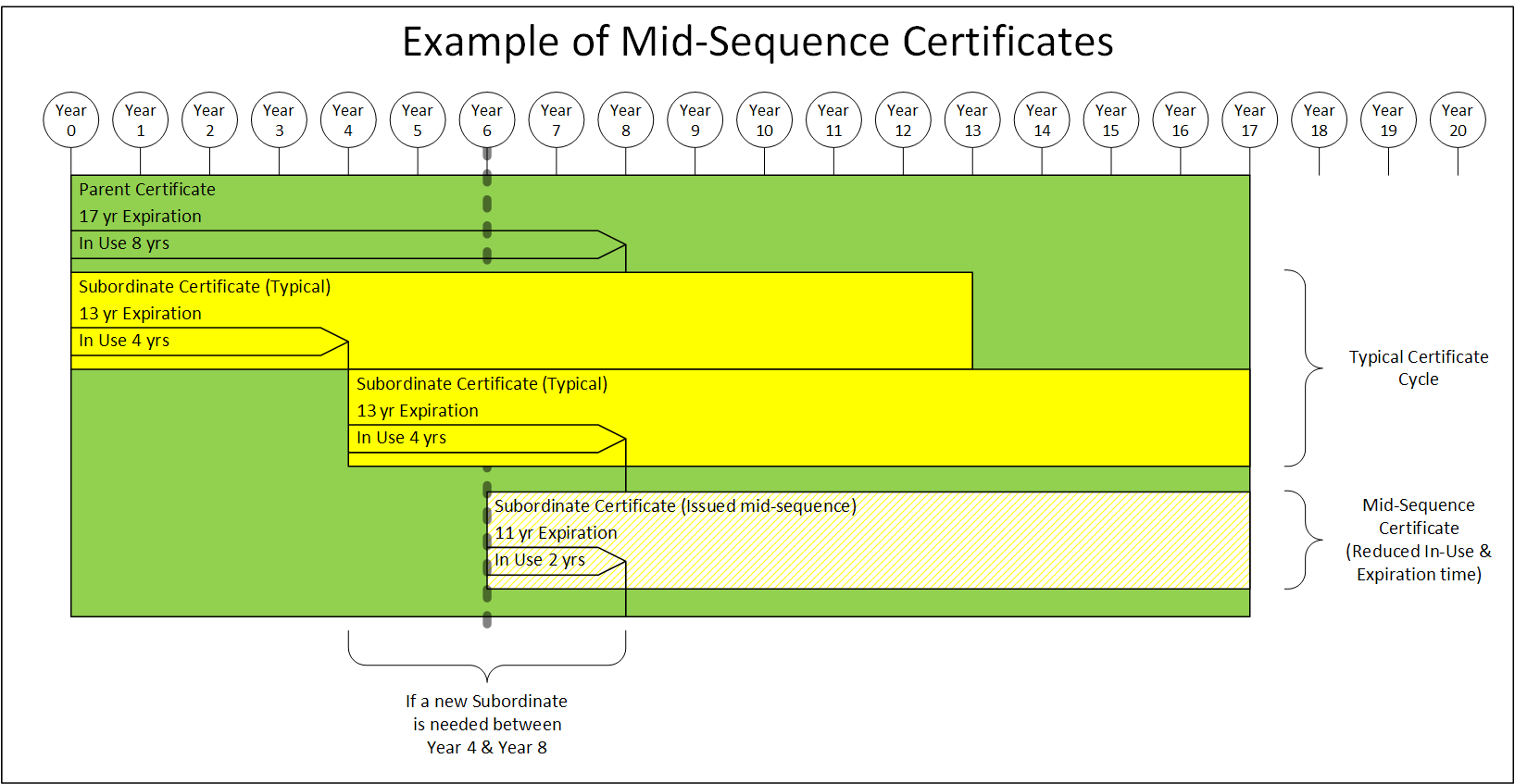
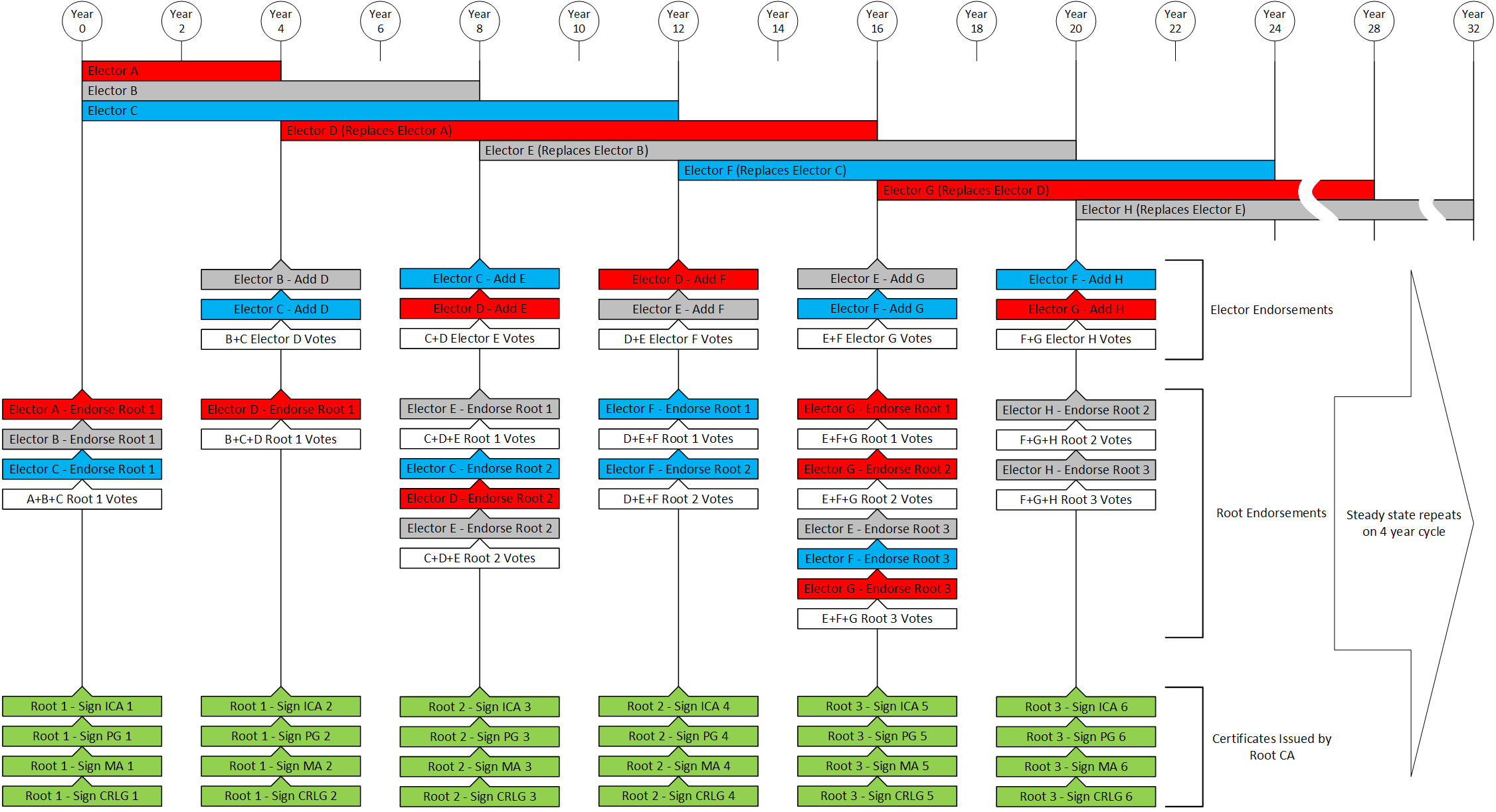
Establishing
a fixed schedule for
the expiration of elector certificates, root CA certificate(s), intermediate CA certificates
and enrollment CA
certificates is recommended to reduce operational complexities. For offline CAs, this
procedure increases
security by minimizing the frequency of required access. Certificates issued in the middle
of this fixed
schedule, due to revocation or new instances, will expire according to the defined schedule
and will have a reduced overall
lifetime due to a shorter in-use lifetime.
The following guidelines shall be followed when component certificates are issued mid-sequence:
- This concept is mandatory for all certificates issued by the root CA and intermediate CA
- The certificate's in-use and expiration shall be reduced by the same amount
To ensure the overall integrity of the SCMS, the minimum and maximum lifetime of each certificate type will be defined and enforced by the SCMS manager policy. Operators will have some amount of flexibility in defining the actual certificate lifetimes.
Certificate Lifetime Overview
The following table provides the certificate expiration and renewal periods to be used in a SCMS that supports EE enrollment certificate rollover.
| Certificate Type |
Issuing CA
|
Expiration
|
In Use
|
Request for Renewal
|
Start of Validity for Renewal
|
Number of Concurrently Valid Certificates (In-Use [+ Legacy]) |
Example Size in Bytes (Certs are
Not Fixed Size)
|
Notes
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBE Enrollment |
ECA |
6 years | 6 years | Anytime (see notes) | 6 years | 1 |
87 |
Rollover certificate will be available no more than 3 years before start of validity. |
| OBE Pseudonym | PCA | 1 week + 1 hour | 1 week | Anytime | 1 week | 20 + 20 (for just 1 hour) |
86 |
|
| OBE Identification | PCA | 1 month + 1 hour | 1 month | Anytime | 1 month | 1 + 1 (for just 1 hour) |
89 |
|
| RSE Enrollment |
ECA |
6 years | 6 years | Anytime (see notes) | 6 years | 1 |
87 |
Rollover certificate will be available no more than 3 years before start of validity. |
| RSE Application | PCA | 1 week + 1 hour | 1 week | Anytime | 1 week | 1 + 1 (for just 1 hour) |
89 |
|
| DCM | ICA | 3 years + 1 week | 3 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 3 years | 1 + 1 (for just 1 week) |
219 |
|
| ECA | ICA | 11 years | 2 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 2 years | 1 + 5 |
150 |
|
| RA | ICA | 3 years + 1 week | 3 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 3 years | 1 + 1 (for just 1 week) | 217 | |
| LA | ICA | 3 years + 1 week | 3 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 3 years | 1 + 1 (for just 1 week) | 205 | |
| PCA | ICA | 4 years | 1 year | 3 months before end of In-Use | 1 year | 1 + 3 | 216 | |
| ICA | Root CA | 13 years | 4 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 4 years | 1 + 3 | 195 | |
| MA | Root CA | 4 years + 1 week | 4 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 4 years | 1 + 1 (for just 1 week) | 205 | |
| CRLG | Root CA | 4 years + 1 week | 4 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 4 years | 1 + 1 (for just 1 week) | 190 | |
| Policy Generator (PG) | Root CA | 4 years + 1 week | 4 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 4 years | 1 + 1 (for just 1 week) | 172 | |
| Root CA (RCA) | Self | 17 years | 8 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 8 years | 1 + 2 | 211 | |
| Elector | Self | 12 years | 12 years | 3 months before end of In-Use | 12 years | 3 | 166 | The initial elector certificates have an expiration and "in use" time of 4, 8 and 12 years, respectively. |
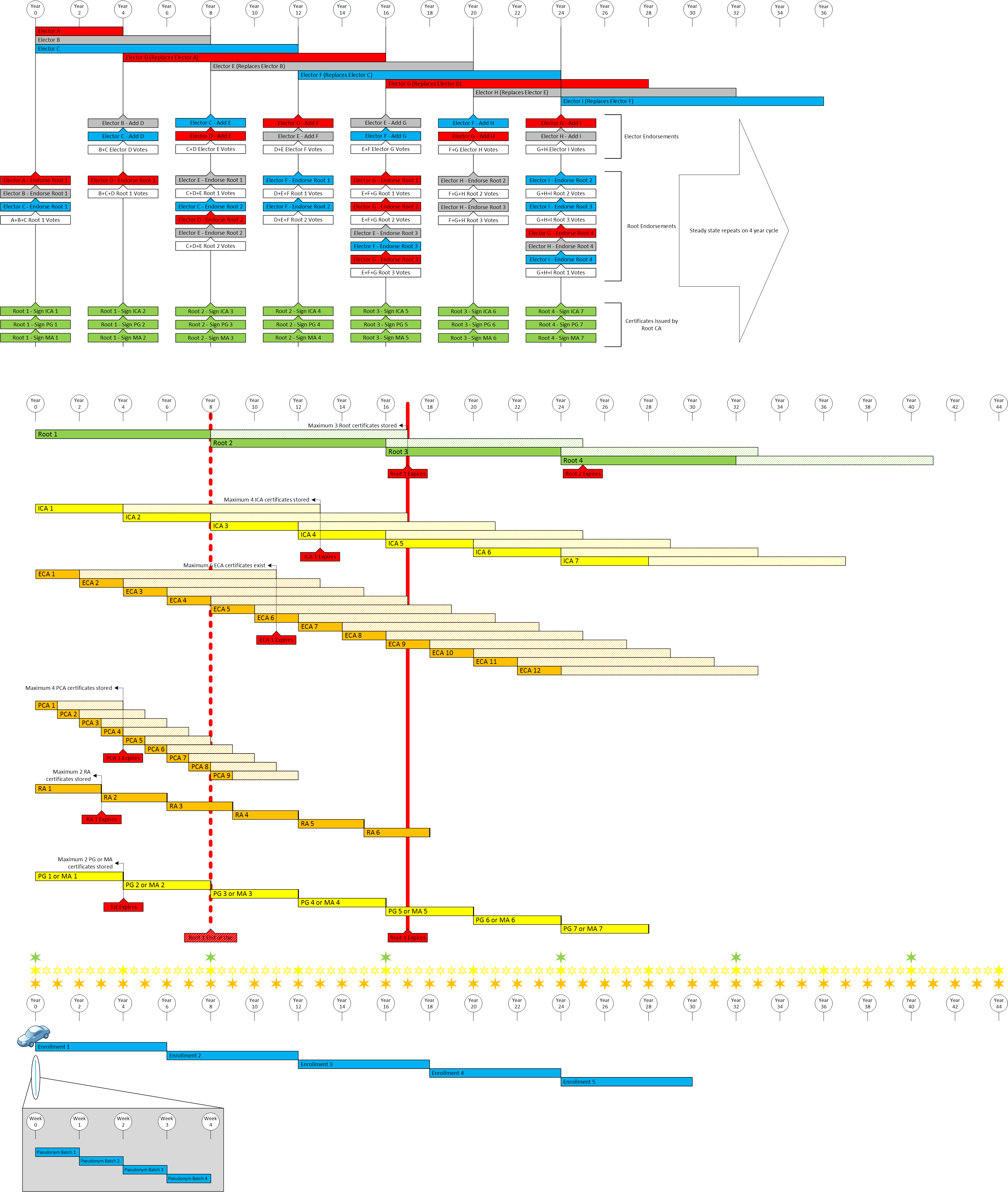
Overview Diagrams
The following diagrams illustrate the expiration period of various certificate types. The diagrams show the specific duration of the certificate (valid from and to dates) only and do not account for setup time (request generation, signing ceremony, distribution, etc.). Each section shows the life of a single instance of a component under typical (non-compromised) conditions. If multiple instances exist, they would follow a similar pattern but the specific dates may be shifted within the validity period.